Non-dental causes of toothache are much less common as compared with dental causes. In a toothache of neurovascular origin, pain is reported in the teeth in conjunction with a migraine. Local and distant structures (such as ear, brain, carotid artery, or heart) can also refer pain to the teeth. Other non-dental causes of toothache include myofascial pain (muscle pain) and angina pectoris (which classically refers pain to the lower jaw). Very rarely, toothache can be psychogenic in origin. Disorders of the maxillary sinus can be referred to the upper back teeth. The posterior, middle and anterior superior alveolar nerves are all closely associated with the lining of the sinus. The bone between the floor of the maxillary sinus and the roots of the upper back teeth is very thin, and frequently the apices of these teeth disrupt the contour of the sinus floor. Consequently, acute or chronic maxillary sinusitis can be perceived as maxillary toothache, and neoplasms of the sinus (such as adenoid cystic carcinoma) can cause similarly perceived toothache if malignant invasion of the superior alveolar nerves occurs. Classically, sinusitis pain increases upon Valsalva maneuvers or tilting the head forward.
Jaw Joint?
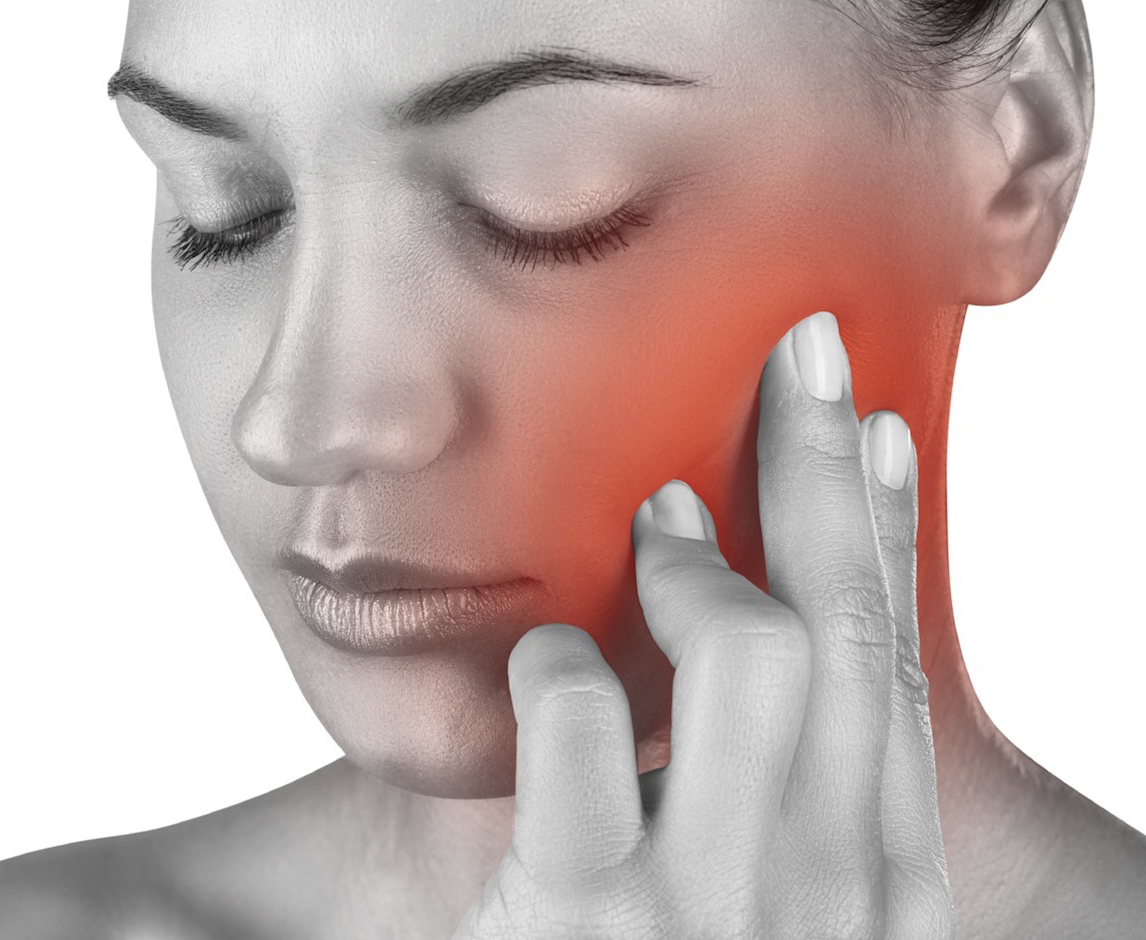
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD, TMJD) is an umbrella term covering pain and dysfunction of the muscles of mastication (the muscles that move the jaw) and the temporomandibular joints (the joints which connect the mandible to the skull). The most important feature is pain, followed by restricted mandibular movement, and noises from the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) during jaw movement. Although TMD is not life-threatening, it can be detrimental to quality of life, because the symptoms can become chronic and difficult to manage.
Tongue?
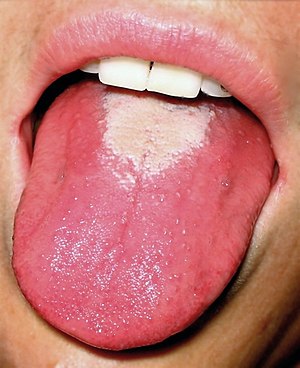
Glossitis can mean soreness of the tongue, or more usually inflammation with depapillation of the dorsal surface of the tongue (loss of the lingual papillae), leaving a smooth and erythematous (reddened) surface, (sometimes specifically termed atrophic glossitis). In a wider sense, glossitis can mean inflammation of the tongue generally. Glossitis is often caused by nutritional deficiencies and may be painless or cause discomfort. Glossitis usually responds well to treatment if the cause is identified and corrected.
Cheeks or lips?
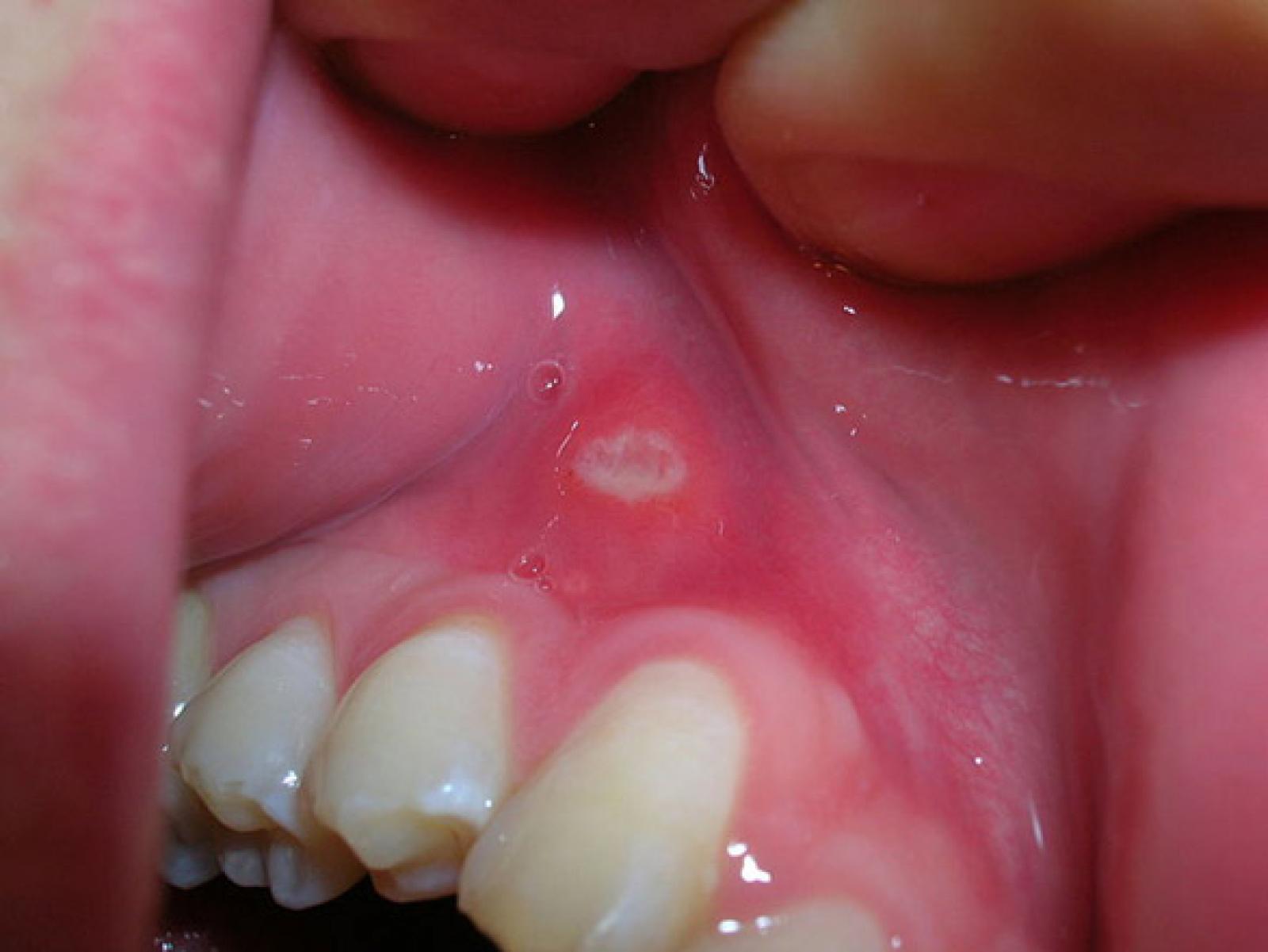
Aphthous stomatitis is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benign and non-contagious mouth ulcers (aphthae) in otherwise healthy individuals. The informal term canker sores is also used, mainly in North America, although this may also refer to any mouth ulcers.These ulcers occur periodically and heal completely between attacks. In the majority of cases, the individual ulcers last about 7–10 days, and ulceration episodes occur 3–6 times per year. Most appear on the non-keratinizing epithelial surfaces in the mouth (i.e. anywhere except the attached gingiva, the hard palate and the dorsum of the tongue), although the more severe forms, which are less common, may also involve keratinizing epithelial surfaces. Symptoms range from a minor nuisance to interfering with eating and drinking.